NOCICEPTIVE PAIN MEANING
Nociceptive refers to pain that is caus by injury or damage to specific tissues or organs in the body. This type of pain is typically associat with inflammation, swelling, and a sharp or dull ache.
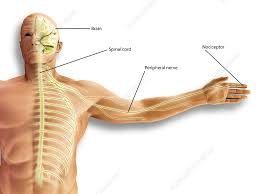
Examples of nociceptive include a broken bone, a sprained ankle, or a toothache. Nociceptive is mediate special nerve fibers known as nociceptors, which transmi signals of pain to the brain.
The pain is usually localiz and can be treat with over-the-counter pain medications or prescription pain medication.
NOCICEPTIVE EXAPLES
Burn pain from touching a hot stove
Cut pain from slicing a finger with a knife
Bone fracture pain from a broken leg
Dental pain from a cavity or tooth extraction
Surgical incision pain from a surgical procedure
Headache pain from a migraine or tension headache
Back pain from a strained muscle or herniated disc
Arthritis pain in the joints
Menstrual cramps
Sunburn pain from excessive sun exposure.
NOCICEPTIVE PAIN TYPES
Superficial nociceptive: This type of pain is caus by injury or damage to the surface of the skin, such as a cut or burn. It is usually sharp and localized.
Deep nociceptive: This type of pain is caus by injury or damage to deeper structures in the body, such as muscles, bones, or organs.
It is usually dull and aching and may be accompanied by muscle spasms or stiffness.
Somatic nociceptive pain: This type of pain is causedby injury or damage to the body’s somatic structures, such as muscles, bones, or joints.
It is usually describ as a sharp or aching pain and can be accompanied by stiffness or muscle spasms.
Visceral nociceptive pain: This type of pain is caus by injury or damage to the body’s internal organs, such as the liver, stomach, or intestines.
It is often describ as a dull, aching pain that is difficult to locate.
Inflammatory nociceptive: This type of pain is caus by inflammation in the body, such as in the case of rheumatoid arthritis or tendinitis.
It is usually describ as a dull, aching pain that is accompanied by swelling and redness.
Examin News
NOCICEPTIV CAUSES
Tissue damage or injury: This type of pain is causedby damage or injury to the body’s tissues, such as a cut, burn, or broken bone.
Inflammation: Inflammation caused by conditions such as arthritis or tendonitis can result in nociceptive pain.
Surgical procedures: Nociceptive pain can occur after surgery as the body heals from the procedure.
Trauma: Trauma to the body, such as a car accident or sports injury, can cause nociceptive pain.
Disease: Certain diseases, such as cancer or kidney stones, can cause nociceptive pain.
Neurological conditions: Nociceptive can be a symptom of certain neurological conditions, such as trigeminal neuralgia or shingles.
Infections: Some infections, such as tooth abscesses or appendicitis, can cause nociceptive.
Mechanical pain: Mechanical pain is caus by the overuse of a particular joint or muscle, such as repetitive strain injury.
Phantom pain: Phantom pain is a type of nociceptive that can occur after an amputation or other loss of a limb.
Thermal pain: Thermal pain is cause by exposure to extreme temperatures, such as frostbite or sunburn.
Also check: vyvanse withdrawal timeline | alcohol and trazodone
NOCICEPTIVE PAIN TREATMENT
Nociceptive is cause by damage or injury to the body’s tissues and can be treat with a variety of methods, including:
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen can help alleviate mild to moderate nociceptive. Prescription medications such as opioids and anti-inflammatory drugs may also be prescrib for more severe pain.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help to alleviate pain by strengthening the muscles and joints, increasing range of motion and reducing inflammation.
Cold and Heat Therapy: Cold therapy can help to reduce inflammation and numb the area, while heat therapy can help to increase blood flow and reduce muscle tension.
Massage: Massage therapy can help to alleviate pain by releasing muscle tension and promoting relaxation.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine practice that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and promote healing.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove damaged tissue, such as a herniated disc or broken bone.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for your specific type of nociceptive.
Best Medicine For Nociceptive pain Tapal 100mg And Tydol 100mg
NOCICEPTIVE VS SOMATIC PAIN
Nociceptive and somatic pain are both types of physical pain, but they have different characteristics and causes.
This type of pain is often describ as sharp, aching, or throbbing.
It is typically localiz to the area of injury and can be accompani by swelling, redness, and warmth.
Nociceptive is the body’s normal response to injury and is necessary for healing to occur.
Somatic pain, on the other hand, is caus by dysfunction or injury to the body’s internal structures, such as muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bones. This type of pain is often describ as dull, achy, or burning.
It may be more diffuse and harder to pinpoint to a specific location. Somatic pain can be caus by conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic back pain.
Both types of pain can be treat with medications, physical therapy, and other interventions. However, the underlying causes of the pain and the specific characteristics of the pain will often determine the most effective treatment approach.
NOCICEPTIVE VS NEUROPATHIC PAIN
Nociceptive and neuropathic pain are two different types of pain that are cause differen mechanisms in the body.
This type of pain is typically describ as sharp, acute, or well-localized. Examples of nociceptive include a broken bone, a cut, or a burn.
Neuropathic pain, on the other hand, is caus by damage or dysfunction in the nervous system. This type of pain is often describ as burning, shooting, or electric-like. Examples of neuropathic pain include diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and phantom limb pain.
Both types of pain can be treat with medication and other forms of therapy, but the treatment approach may differ depending on the underlying cause of the pain. Nociceptive may respond