DVT (deep vein thrombosis or thrombus) is a severe medical condition that can cause significant pain and discomfort. The best way to avoid it is to take preventative measures, such as wearing compression stockings and avoiding prolonged bed rest following surgery. However, several treatment options are available if you do develop DVT. DVT treatment depends on the severity of your condition. Your doctor will also take into consideration what caused your DVT. You can consider getting vein treatment in Melbourne if you reside in Australia.
The following article will explain DVT, its symptoms, and possible treatment options.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that can lead to pulmonary embolism (PE), a blockage of an artery in the lung.
DVT is not fatal if it does not embolise. However, in the acute setting (less than two weeks after a clot has formed), blood clots are more likely to break loose and embolise to the lung – this can be fatal.
Your doctor will perform a physical examination and ask you questions about your symptoms as well as request some investigations (including blood tests and ultrasounds or CT scans) to get a diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis.
After the first few weeks, the DVT becomes ‘chronic’. This can cause chronic, intermittent limb discomfort and edema in as much as 50% of sufferers. This condition is known as post-thrombotic syndrome.
Some of the symptoms of post-thrombotic syndrome are:
- Leg swelling and aching, which may deteriorate towards the end of the day.
- Brown skin pigmentation or discolouration, particularly around the ankles.
- Leg ulceration
Who Is at Greater Risk For DVT?
People who have recently had surgery or major injury are at greater risk for developing DVT. Other people who are at higher risk include:
- Women taking birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy, or estrogen therapy for menopause
- Smokers and those who have quit smoking within the past year
- People with cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, or other chronic inflammatory conditions
- People with clotting disorders or a family history of clotting disorders
- Trauma to the legs
What Is the Treatment for Deep Vein Thrombosis?
The treatment for this condition depends on several factors, such as the symptoms’ severity, the DVT’s location, the duration since onset, and whether any other underlying health problems require treatment. Some people may need intervention to remove the clot. Others may need medication to dissolve the clot or prevent further clots from forming. A vascular surgeon will be able to advise on the best treatment for each circumstance.
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) treatment is a type of vein treatment that aims to decrease morbidity, avoid or lessen the likelihood of developing postthrombotic syndrome, and avert pulmonary embolism (PE).
Here’s what you can expect in DVT treatment if you’re diagnosed with it:
1. Anticoagulants
If you have an uncomplicated case, your doctor may prescribe blood-thinning drugs called anticoagulants, which work by preventing clots from extending further in your veins.
A blood thinner can be taken orally, intravenously, or injected subcutaneously. Drugs that thin the blood are commonly used to treat deep vein thrombosis. You and your doctor may weigh the pros and cons of each option and choose the best course of action.
You may need to take blood-thinning medication for 3-6 months. Take them exactly as directed to reduce the risk of adverse reactions.
2. Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter
A filter can be placed into the inferior vena cava (a major vein that sends blood back to the heart) to collect or trap an embolus (a clot travelling through the vein) before reaching the lungs. This is done when anticoagulants cannot be used or do not function well enough. Inferior vena cava (IVC) filters are little metal devices that appear like an upside-down umbrella that can prevent blood clots from travelling through your veins.
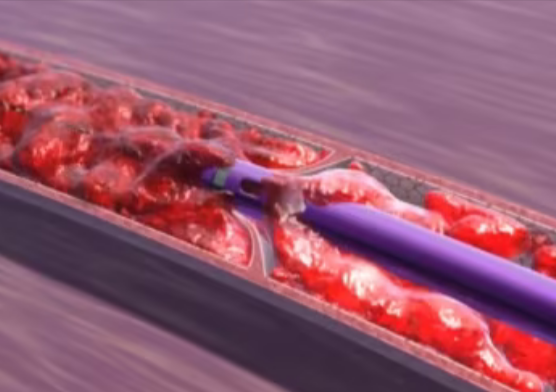
3. Clot Busters (Thrombolytics)
DVT thrombolysis is a minimally invasive therapy used to quickly alleviate symptoms and remove the clot from the deep veins in patients with acute DVT who have big clots.
Procedures for thrombolysis of deep vein thrombosis require the insertion of a catheter into the affected leg under ultrasound or x-ray guidance. Mechanical devices and drugs that dissolve clots can be placed into the catheter to remove or shrink the clot. A vascular surgeon will be able to advise whether this is appropriate for you, and they will be able to perform this procedure if required.
4. Compression Stockings
These stretchy stockings apply pressure to the legs to help prevent clots. They are also used to treat leg swelling if you have a DVT.
Takeaway
DVT is a serious condition and not one to be taken lightly. It can have life-threatening consequences if left untreated. However, the good news is that several treatments can help you recover from DVT and reduce your risk of the condition recurring.
If you have been diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis, you must speak with your doctor about the available treatment options.
Read more article on Examinnews